Micropipette: Introduction, Types, and Usage Guide
A micropipette is a precision laboratory tool designed for measuring and transferring small liquid volumes with high accuracy. This versatile instrument is used extensively in scientific research to handle minute quantities of liquids, especially in fields like biology, chemistry, and medical diagnostics.
What is a Micropipette?
Micropipettes are specialized pipettes used to measure and transfer very small volumes, typically from 0.1 µL to 1000 µL. They work by displacing air or using a piston to draw in and dispense liquids. They are essential for many laboratory applications, particularly in research and medical testing, providing precision and accuracy in measurements.
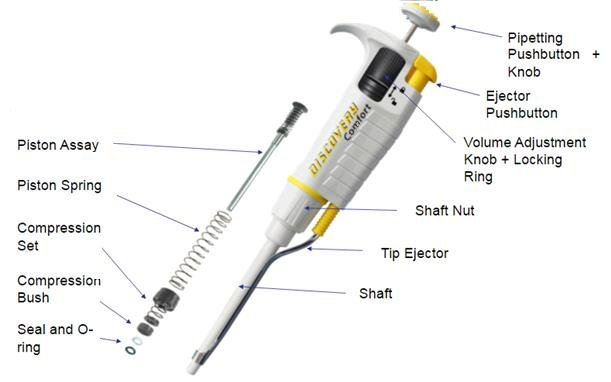
What are the Key Components of a Micropipette?
The main components of a micropipette include:
- Plunger: Used to draw and release the liquid.
- Volume Adjustment Dial: Allows users to set the exact volume to be measured.
- Tip Ejector: Used to safely remove the tip after use.
- Micropipette Tip: Disposable tips of various sizes to handle different volumes.
How Do Micropipettes Work?
Micropipettes operate by using a piston or air displacement mechanism. When the plunger is pressed, the internal piston draws in the liquid into the tip. After setting the correct volume, the plunger is pressed again to release the liquid into the desired container.
What Types of Micropipettes Are Available?
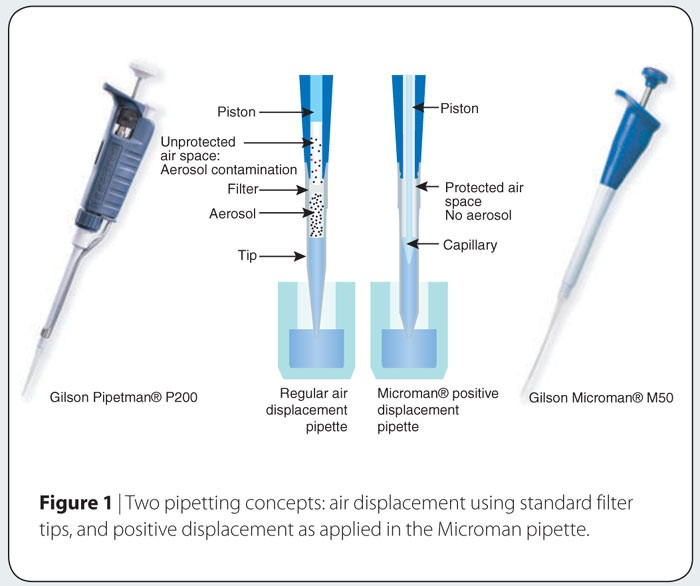
- Air Displacement Micropipettes: Most common type, precise for measuring volumes from 0.1 µL to 5000 µL.
- Positive Displacement Micropipettes: Used for highly viscous liquids or non-aqueous solutions.
- Electronic Micropipettes: These micropipettes provide automatic volume adjustments and reduce human error.
- Multi-Channel Micropipettes: Used to handle multiple samples simultaneously, ideal for high-throughput experiments.
How Do You Use a Micropipette?
To use a micropipette effectively:
- Attach the Appropriate Tip: Choose the correct tip size for your volume.
- Set the Volume: Adjust the volume using the dial and check the digital readout.
- Draw the Liquid: Press the plunger to the first stop, immerse the tip into the liquid, and slowly release the plunger to fill the tip.
- Dispense the Liquid: Place the tip into the receiving vessel, press the plunger to the second stop to ensure all the liquid is dispensed.
What Are the Different Pipetting Techniques?
- Forward Pipetting: Liquid is drawn into the tip and dispensed by pressing the plunger to the second stop.
- Reverse Pipetting: Commonly used for volatile liquids, where liquid is drawn in and dispensed from the second stop to avoid contamination.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235981319_The_Art_of_Pipetting
How Can You Prevent Contamination While Using a Micropipette?
To prevent cross-contamination:
- Always use a fresh tip for each sample.
- Avoid touching the tip with your hands.
- Clean the micropipette regularly to ensure accurate performance.
What is the Difference Between Single-Channel and Multi-Channel Micropipettes?
A single-channel micropipette is used to transfer one sample at a time, while a multi-channel micropipette allows for transferring multiple samples simultaneously, enhancing efficiency in high-throughput applications.
What Types of Micropipette Tips Are Available?
- White Micropipette Tips: Used for very small volumes (P2, P10, P20).
- Yellow Micropipette Tips: Suitable for medium volumes (P100, P200).
- Blue Micropipette Tips: Designed for larger volumes (P1000 and above).
Why is Micropipette Calibration Important?
Micropipettes must be calibrated regularly to ensure accuracy. Calibration involves using a balance to measure the dispensed volume and adjusting the pipette based on the readings. Regular calibration ensures reliable results and minimizes errors in experiments.
By understanding how to properly use and maintain a micropipette, researchers can ensure high accuracy in their scientific work, leading to more reliable and reproducible results.